Comprehensive Guide to the Top World Fighter Jets
Advanced fighter jets represent the pinnacle of technological progress in military aviation, combining speed, stealth, cutting-edge avionics, and powerful weapons to achieve air superiority. Top World Fighter Jets, the Boeing F-47, Lockheed Martin F-35, Sukhoi Su-57, Chengdu J-20, Mitsubishi F-X, Rafale Dassault, and F/A-XX are thoroughly and easily analyzed in this article. We’ll examine their technology, defense systems, combat capabilities, generational developments, stock market effects on their makers, worldwide usage patterns, and identify the most potent jet overall. We’ll also go over often asked questions to make sure you fully understand.
1. Boeing F-47: The Pinnacle of Sixth-Generation Advanced Fighter Jets
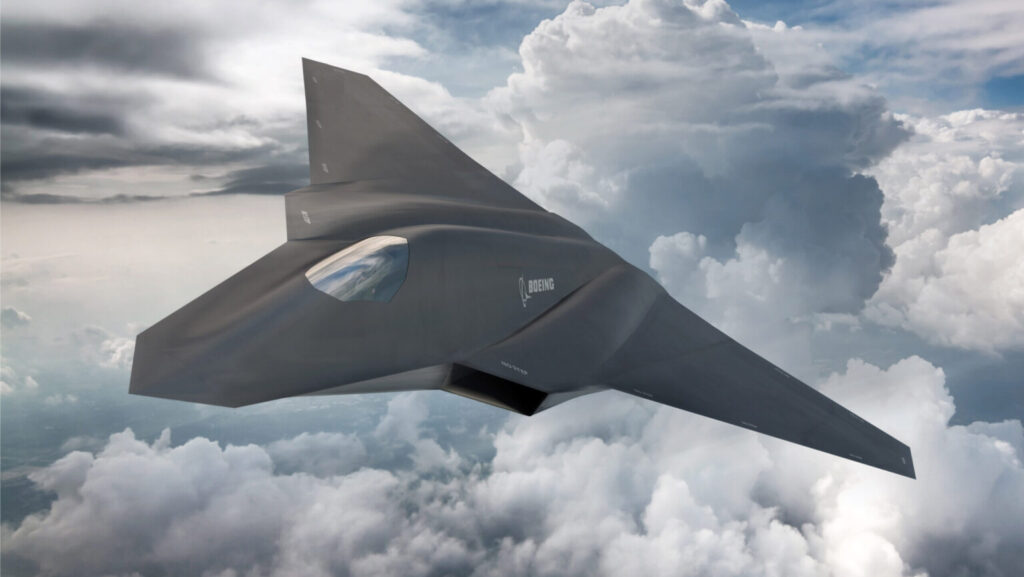

The F-22 Raptor will be replaced by the sixth-generation F-47 Boeing, which was created as part of the U.S. Air Force’s Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program.
President Trump made an official announcement on the Boeing F-47 fighter jet, saying, “President Trump announces Boeing will build the F-47 fighter jet.” A major change was signaled by this news, since Boeing won the contract instead of Lockheed Martin. The strategic significance of the Boeing F-47 is shown by its awarding of the U.S. Air Force’s NGAD contract.
Technology and Features
With the use of modern components and shape, the F-47’s Stealth++ technology makes it nearly invisible to radar. Real-time data processing and sensor fusion are made possible by its AI-driven avionics, which combine inputs from electrical, radar, and infrared sensors. For increased mission flexibility, the jet can coordinate with drones and support manned-unmanned teaming.
Combat Capabilities
With a maximum velocity of almost Mach 2 (1,500+ mph), the F-47 is built for quick intercepts. Long-range operations are guaranteed by its battle radius of more than 1,000 nautical miles. The jet provides accuracy and lethality in air-to-air and air-to-ground missions by carrying laser-based weapons and hypersonic missiles.
Defense Systems
The F-47’s directed-energy weaponry destroys incoming missiles, while its electronic countermeasures (ECM) jam enemy radar. Its stealth profile increases survivability in contested areas by reducing detection.
Generational Advantage
As a sixth-generation fighter, the F-47 integrates AI, drone collaboration, and network-centric warfare, surpassing fifth-generation capabilities in adaptability and connectivity.
Operational Status
Currently in development, the F-47 is slated for service between 2027 and 2029, with the U.S. Air Force planning to acquire over 185 units.
2. Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II: The Global Standard in Advanced Fighter Jets
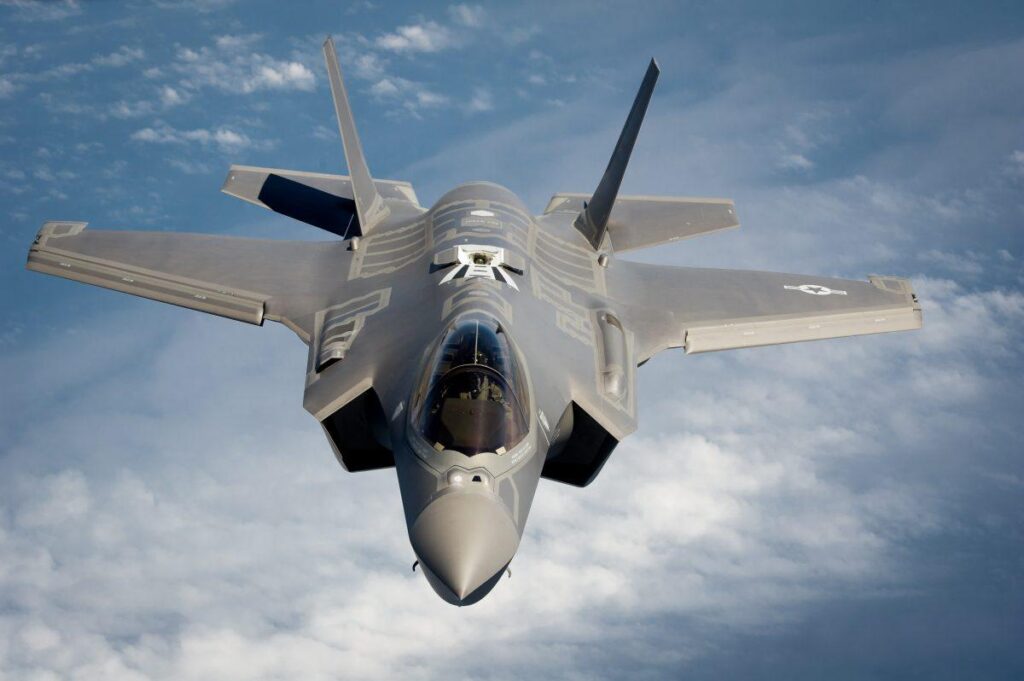

The Lockheed Martin F-35 is a fifth-generation multirole stealth fighter, serving the U.S. military and allies like the UK, Japan, and Australia.
Technology and Features
For stealth, the F-35 uses materials that absorb radar and a low-observable design. By combining data from several sensors, its sensor fusion gives pilots a complete picture of the battlefield. It is quite adaptable and comes in three different versions: the carrier-based F-35C, the short takeoff/vertical landing F-35B, and the normal takeoff F-35A.
Combat Capabilities
Reaching Mach 1.6 (1,200 mph), the F-35 has a combat radius of ~1,000 nautical miles. It carries air-to-air missiles, precision-guided bombs, and anti-ship munitions, excelling in diverse missions.
Defense Systems
The Distributed Aperture System (DAS) detects missile launches, while the electronic warfare suite disrupts enemy radar. Stealth features reduce its radar cross-section, enhancing survivability.
Generational Advantage
A fifth-generation fighter, the F-35 excels in stealth, multirole versatility, and interoperability, making it a cornerstone for allied air forces.
Operational Status
In active service, over 900 F-35s are deployed globally, with Lockheed Martin addressing production backlogs to deliver 180 units in 2025.
The Lockheed Martin F-35 contract has been a significant contributor to the company’s revenue, with recent contracts valued at billions of dollars. Despite some production delays, the F-35 remains a cornerstone of modern air forces.
3. Sukhoi Su-57: Russia’s Stealth Advanced Fighter Jet
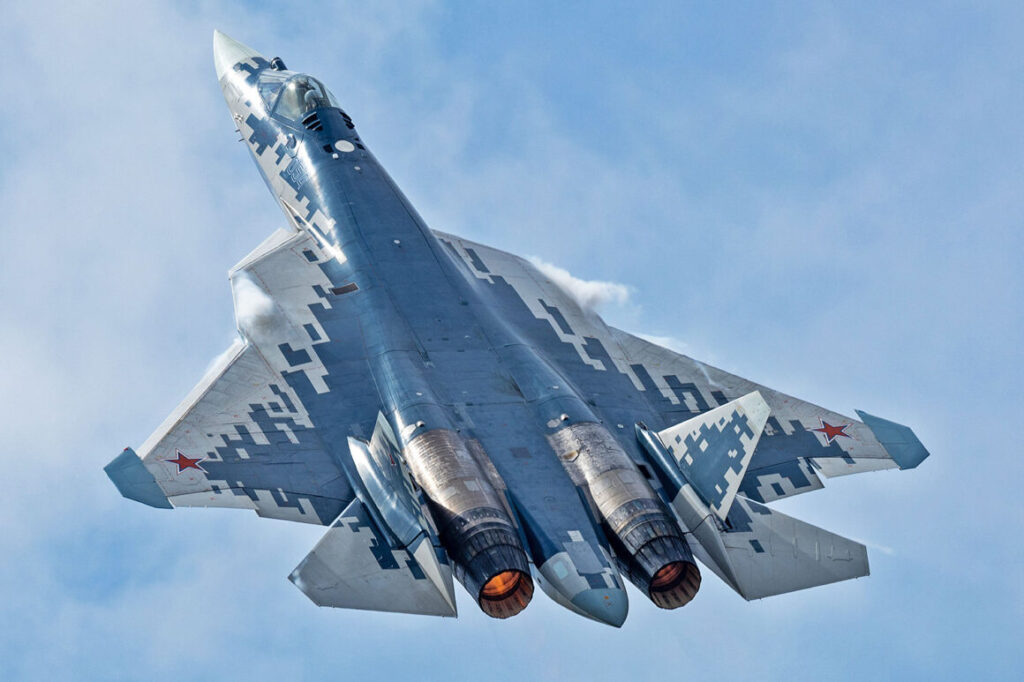

The Sukhoi Su-57, Russia’s first fifth-generation stealth fighter, aims to compete with Western counterparts. Recently, Russia receives new Sukhoi Su-57 and Su-34 fighter jets, bolstering its air force capabilities.
Technology and Features
The Su-57 features a reduced radar cross-section and infrared signature suppression. Its active phased-array radar and thrust-vectoring engines enable supermaneuvrability, allowing complex aerial maneuvers.
Combat Capabilities
Capable of Mach 2, the Su-57 has a combat radius of ~1,500 km. It carries air-to-air missiles, hypersonic weapons, and precision-guided munitions, balancing air superiority and ground attack roles.
Defense Systems
Electronic countermeasures disrupt enemy targeting, while stealth features reduce detectability. Onboard sensors provide missile warnings and deploy countermeasures.
Generational Advantage
As a fifth-generation fighter, the Su-57 emphasizes “functional stealth,” balancing low observability with aerodynamic performance.
Operational Status
In limited service with the Russian Air Force, the Su-57 faces production delays but has seen recent deliveries. Its combat use in Ukraine has been limited, raising questions about effectiveness.
4. Chengdu J-20: China’s Stealth Advanced Fighter Jet
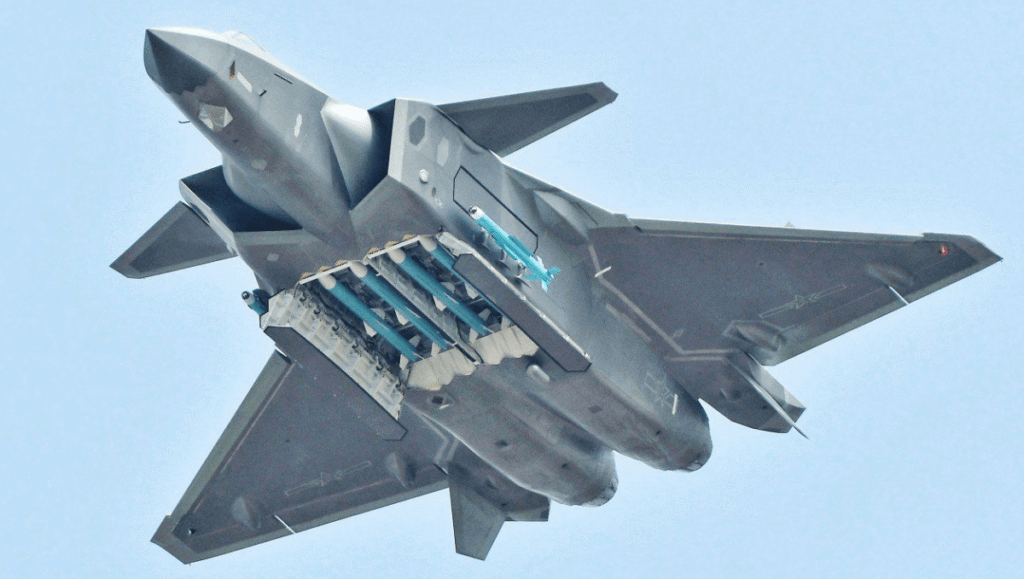

The Chengdu J-20, China’s fifth-generation stealth fighter, is designed for air dominance.
Technology and Features
The J-20’s stealth design uses advanced shaping and materials. Equipped with AESA radar and sensor fusion, it maintains situational awareness. Internal weapons bays preserve its low radar signature.
Combat Capabilities
Estimated at Mach 2, the J-20’s combat radius is classified but substantial. It carries long-range air-to-air missiles (e.g., PL-15) and air-to-ground munitions, optimized for penetration missions.
Defense Systems
Electronic warfare systems counter radar and missiles, while stealth enhances survivability. Advanced sensors detect threats early.
Generational Advantage
A fifth-generation fighter, the J-20 focuses on frontal stealth and long-range capabilities, positioning China as a global aviation power.
Operational Status
In active service with over 200 units operational, the J-20 continues to evolve with new variants, including a two-seater for drone control.
5. Mitsubishi F-X: Japan’s Next-Generation Advanced Fighter Jet

The Mitsubishi F-X is Japan’s sixth-generation fighter, emphasizing stealth and electronic warfare.
Technology and Features
For increased stealth, the F-X makes use of metamaterials and plasma stealth antenna technologies. Comprehensive awareness is provided by its infrared cameras, passive RF sensors, and AESA radar. It is made to integrate drones.
Combat Capabilities
Performance metrics are TBD, but the F-X is expected to be agile, carrying hypersonic missiles and precision munitions for multirole missions.
Defense Systems
Microwave weapons disrupt enemy missiles, and advanced ECM jams radar. Stealth systems ensure minimal detectability.
Generational Advantage
A sixth-generation fighter, the F-X prioritizes drone collaboration, electronic warfare, and next-gen stealth, aligning with Japan’s defense strategy.
Operational Status
In development, the F-X is targeted for deployment in the 2030s by the Japan Air Self-Defense Force.
6. Dassault Rafale: France’s Omnirole Advanced Fighter Jet

The Dassault Rafale, a 4.5-generation multirole fighter, is renowned for its versatility.
Technology and Features
Powered by two Snecma M88 engines, the Rafale achieves supercruise. Its multisensor data fusion integrates radar, infrared, and electronic inputs. Smart sensors enhance targeting.
Combat Capabilities
With a top speed of Mach 1.8, the Rafale’s combat radius is 1,850 km. It carries air-to-air missiles, nuclear weapons, and anti-ship munitions, excelling in diverse roles.
Defense Systems
The SPECTRA system provides electronic countermeasures and missile warnings. Its reduced radar cross-section improves survivability, though not fully stealthy.
Generational Advantage
A 4.5-generation fighter, the Rafale bridges fourth and fifth-generation capabilities with advanced avionics and multirole flexibility.
Operational Status
In active service with France, India, Egypt, and others, the Rafale has proven its combat prowess in Afghanistan, Libya, and Mali.
7. F/A-XX: The U.S. Navy’s Future Advanced Fighter Jet

The F/A-XX is the U.S. Navy’s sixth-generation fighter, designed to replace the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet.
Technology and Features
The F/A-XX program will feature next-generation stealth and advanced sensors. Its networking capabilities enable integration with naval assets, supporting manned-unmanned teaming.
Combat Capabilities
Performance details are TBD, but the F A XX will excel in air combat, ground attack, and electronic warfare, carrying advanced munitions.
Defense Systems
Directed-energy weapons and ECM will counter threats, with stealth ensuring survivability.
Generational Advantage
A sixth-generation fighter, the F/A-XX emphasizes AI, stealth, and connectivity for future naval operations.
Operational Status
In development, the F/A-XX is planned for service in the 2030s, with ongoing contract reviews.
Recent reports indicate that the US Navy F/A-XX contract is under review, with potential delays in the program’s timeline.
Aviation Stock Market Analysis for Advanced Fighter Jet Manufacturers
The production of top world Fighter Jets significantly impacts the stock market performance of their manufacturers. Below is an analysis of key players based on recent trends and events.
Boeing (F-47)
Investor trust has increased when Boeing was chosen for the NGAD program, and the F-47 contract indicates long-term income potential. Despite more general difficulties in commercial aviation, Boeing’s shares increased by almost 10% in 2024 after the announcement. About 40% of the company’s revenue comes from its military aviation division, which includes the F-15EX and F/A-18, stabilizing its portfolio.
Lockheed Martin (F-35)
Lockheed Martin’s F-35 program generates billions of dollars in revenue from contracts. It anticipates delivering 180 F-35s by 2025, thereby resolving production backlogs. With a 5% rise in 2024, its stock has stayed steady, indicating robust demand from the United States and its allies. However, the hefty operational costs of the F-35 cast doubt on its long-term viability.
United Aircraft Corporation (Sukhoi Su-57)
Economic limitations are preventing Russia’s United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) from producing as many Su-57s. Russia’s state-controlled market makes stock performance less transparent, but UAC’s finances have been squeezed by sanctions and restricted exports. Its market position has not been greatly altered by recent Su-57 deliveries.
Chengdu Aircraft Industrial Group (J-20)
Following news of J-10C victories in the India-Pakistan conflict, Chengdu’s shares rose 60% in May 2025, indicating investor confidence in China’s aircraft industry. With more than 200 produced, the J-20 highlights China’s expanding market share and challenges Western hegemony.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (F-X)
Mitsubishi’s aerospace division benefits from Japan’s defense investments. The F-X program has driven a 15% stock increase in 2024–2025, with analysts projecting growth as Japan expands its military capabilities.
Dassault Aviation (Rafale)
Dassault’s stock experienced volatility, dropping 7% in May 2025 when Pakistan’s J-10C downs Indian Rafale in historic clash in Operation Sindoor, but rebounded 3% as India confirmed additional orders for 26 Rafale M jets. The Rafale’s export success to India, Egypt, and Qatar supports Dassault’s market resilience.
Aviation Stock Market and Jet Comparison
Stock Market Trends (2024–2025)
- Boeing: +10% stock rise post-F-47 NGAD contract; ~40% revenue from military aviation.
- Lockheed Martin: +5% stock growth; F-35 deliveries to reach 180 units in 2025.
- United Aircraft Corporation: Limited stock transparency; constrained by sanctions.
- Chengdu Aircraft: +60% stock surge after J-10C success; J-20 production exceeds 200 units.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries: +15% stock increase driven by F-X program.
- Dassault Aviation: -7% drop, +3% rebound; supported by Rafale exports.
Most Powerful Jet Comparison
| Feature | Boeing F-47 | F-35 | Su-57 | J-20 | F-X | Rafale | F/A-XX |
| Generation | 6th | 5th | 5th | 5th | 6th | 4.5th | 6th |
| Stealth | Stealth++ | Advanced | Functional | Frontal | Plasma | Reduced RCS | Next-gen |
| Speed | Mach 2+ | Mach 1.6 | Mach 2 | Mach 2 | TBD | Mach 1.8 | TBD |
| Combat Radius | 1,000 nm | 1,000 nm | 1,500 km | Classified | TBD | 1,850 km | TBD |
| Avionics | AI-driven | Sensor fusion | Phased-array | AESA | AESA+ | Multisensor | Advanced |
| Weaponry | Hypersonic | Precision | Hypersonic | Long-range | Hypersonic | Nuclear | Advanced |
| Defense Systems | ECM, Lasers | DAS, EW | ECM | EW | Microwave | SPECTRA | Directed-energy |
| Drone Integration | Yes | Limited | No | Yes (new variants) | Yes | No | Yes |
Global Usage Trends of Top World Fighter Jets
Boeing F-47
- Country: U.S. Air Force (NGAD program).
- Trend: High anticipation for its 2027–2029 deployment, with focus on replacing aging F-22s. Trending in U.S. defense circles for its sixth-generation capabilities.
Lockheed Martin F-35
- Countries: U.S., UK, Japan, Australia, Israel, NATO allies.
- Trend: The F-35 is the most widely used advanced fighter jet, with over 2,000 units in service or on order. High demand in NATO countries and Asia-Pacific, particularly Japan and Australia.
Sukhoi Su-57
- Country: Russia.
- Trend: Limited deployment due to production issues. Trending in Russian media for recent deliveries, but its combat role in Ukraine is minimal, reducing global interest.
Chengdu J-20
- Country: China (PLAAF).
- Trend: Growing prominence in Asia, especially after J-10C’s reported success in regional conflicts. The J-20’s stealth and drone-control variants are trending in Chinese defense discussions.
Mitsubishi F-X
- Country: Japan.
- Trend: Significant interest in Japan and Indo-Pacific defense forums, driven by Japan’s push for indigenous technology. Expected to counter regional threats from China and North Korea.
Dassault Rafale
- Countries: France, India, Egypt, Qatar, Greece, UAE.
- Trend: Strong export success, particularly in India, where Rafales were used in Operation Sindoor. High visibility in South Asia and Middle East defense markets.
F/A-XX
- Country: U.S. Navy (future).
- Trend: Emerging interest in naval aviation communities, with focus on its 2030s deployment to counter China’s carrier-based stealth jets.
Which Advanced Fighter Jet Is the Most Powerful?
To determine the most powerful jet, we evaluate stealth, speed, combat radius, avionics, weaponry, defense systems, and additional features (e.g., drone integration).
- Stealth: The boeing fighter jets F 47 Stealth++ technology surpasses the F-35’s advanced stealth, Su-57’s functional stealth, J-20’s frontal stealth, F-X’s plasma stealth, Rafale’s reduced RCS, and F/A-XX’s next-gen stealth (TBD).
- Speed: The F-47, Su-57, and J-20 reach Mach 2, outpacing the F-35 (Mach 1.6) and Rafale (Mach 1.8). F-X and F/A-XX speeds are TBD.
- Combat Radius: The Rafale leads with 1,850 km, followed by the Su-57 (1,500 km), F-47, and F-35 (1,000 nm). J-20’s radius is classified; F-X and F/A-XX are TBD.
- Avionics: The F-47’s AI-driven avionics and F-X’s AESA+ systems are the most advanced, followed by the F-35’s sensor fusion, J-20’s AESA, Su-57’s phased-array, Rafale’s multisensor, and F/A-XX’s advanced systems (TBD).
- Weaponry: The F-47, F-X, and F/A-XX support hypersonic missiles, while the Su-57 and J-20 carry hypersonic and long-range munitions. The F-35 uses precision munitions, and the Rafale supports nuclear weapons.
- Defense Systems: The F-47’s lasers and F/A-XX’s directed-energy weapons lead, followed by the F-X’s microwave weapons, F-35’s DAS/EW, J-20’s and Su-57’s EW, and Rafale’s SPECTRA.
- Drone Integration: The F-47, F-X, F/A-XX, and J-20 (new variants) support drones, while the F-35, Su-57, and Rafale do not.
FAQs About Advanced Fighter Jets
1. What defines an advanced fighter jet?
Advanced fighter jets feature stealth, advanced avionics, sensor fusion, and multirole capabilities. Sixth-generation jets add AI, drone integration, and network-centric warfare.
2. Which jet is the most powerful in 2025?
The fighter jet Boeing F 47 is the most powerful due to its sixth-generation features, including Stealth++ technology, AI-driven avionics, and hypersonic weapons.
3. How does stealth technology work?
Stealth reduces radar and infrared signatures using special materials, shapes, and coatings, making jets harder to detect.
4. What’s the difference between fifth and sixth-generation jets?
Fifth-generation jets emphasize stealth and sensor fusion. Sixth-generation jets add AI, drone collaboration, and advanced electronic warfare.
5. Which jet has the largest global deployment?
The Lockheed Martin F-35, with over 900 units in service across multiple countries, is the most deployed.
6. Which advanced fighter jet is the fastest?
The Boeing F-47, Sukhoi Su 57, and Chengdu J 20 reach Mach 2, the fastest among current jets. F-X and F/A-XX speeds are TBD.
7. How much do advanced fighter jets cost?
Costs vary: F-35 (~$80–110 million), Rafale (~$125 million), Su-57 (~$40–50 million), J-20 (~$100 million). F-47, F-X, and F/A-XX costs are speculative.
8. Which countries use the most advanced fighter jets?
The U.S. (F-35, F-47, F/A-XX), China (J-20), Russia (Su-57), Japan (F-X), France, and India (Rafale) lead in deployment and development.
9. Are advanced fighter jets equipped with AI?
Yes, sixth-generation jets (F-47, F-X, F/A-XX) use AI for decision-making and drone coordination. Fifth-generation jets (F-35, J-20) use AI for data processing.
10. Which jet is best for air superiority?
The Boeing F-47, with its Stealth++ technology, AI-driven systems, and hypersonic missiles, is best suited for air superiority, though the F-35’s versatility makes it a strong contender.
Conclusion
The future of aerial battle is being shaped by advanced fighter planes, which are the pinnacle of military technology. With its sixth-generation features, the Boeing F-47 is the most potent aircraft, but the Lockheed Martin F-35 is widely used. These characteristics are reflected in the financial market, as Dassault manages volatility while manufacturers like Boeing and Chengdu benefit from their jet programs. The competition for air supremacy heats up as countries like the US, China, and Japan invest in these platforms, indicating more advancements in aviation.